컴굥일지
[모션인식] Django에서 OpenPose로 실시간 자세 검출하기 본문
1. OpenPose with Django
저희 팀은 백엔드로 Django를 사용하기로 했습니다.
그래서 AI파트도 Django로 작성하면 나중에 배포할 때 좀 편하지 않을까 싶었습니다.
그러나 생각보다 예시 코드가 많지 않았습니다.
저번 포스트에서 적은 코드는, 새로운 창을 띄워서 거기에 웹캠 영상이 송출되는 방식이었습니다.
하지만 제가 원하는 방식은 아래 사진과 같이 웹페이지에 한 부분에서 동영상이 송출되는 방식입니다.
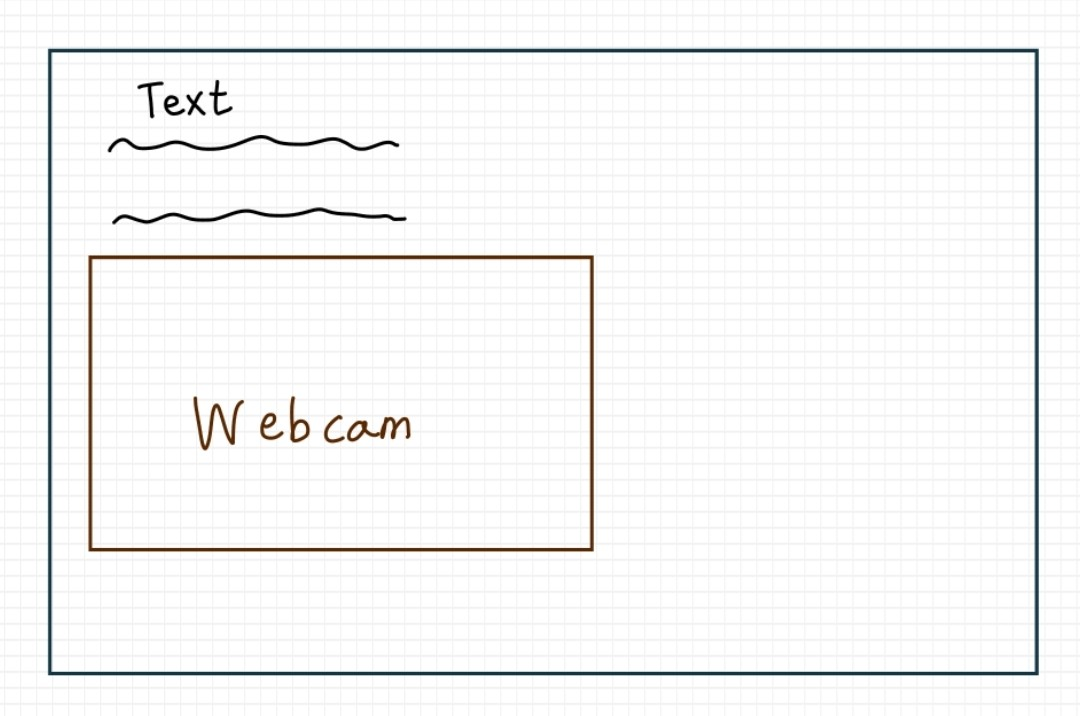
이와 관련된 코드에 대해 아래에 기술하도록 하겠습니다.
2. Django에서 카메라 켜기
일단 먼저 django에서 카메라를 키는 코드를 알아보겠습니다.
#urls.py
from django.urls import path
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
path('',views.home,name="home"), # 웹사이트 링크 home.html
path("detectme",views.detectme,name="detectme"), # 웹캠 링크
]
아래는 home.html 코드입니다.
img 태그 안에 웹캠을 켜는 링크 주소를 넣으면 됩니다.
<!-- home.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Video...</h1>
<table>
<tr>
<td>
<img
src="http://127.0.0.1:8000/detectme"
style="width: 320px; height: 240px"
/>
</td>
<td>나의 비디오...</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
아래는 views.py 코드입니다.
home.html을 render 하고, detectme도 render 하는 코드가 모두 여기 있습니다.
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.views.decorators import gzip
from django.http import StreamingHttpResponse
import cv2
import threading
# home.html
def home(request):
return render(request,"home.html") #home.html을 호출해서 띄워준다.
#카메라 관련 클래스
class VideoCamera(object):
def __init__(self):
self.video = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
(self.grabbed, self.frame) = self.video.read()
threading.Thread(target=self.update, args=()).start()
def __del__(self):
self.video.release()
def get_frame(self):
image = self.frame
_, jpeg = cv2.imencode('.jpg', image)
return jpeg.tobytes()
def update(self):
while True:
(self.grabbed, self.frame) = self.video.read()
def gen(camera):
while True:
frame = camera.get_frame()
# frame단위로 이미지를 계속 반환한다. (yield)
yield(b'--frame\r\n'
b'Content-Type: image/jpeg\r\n\r\n' + frame + b'\r\n\r\n')
# detectme를 띄우는 코드(여기서 웹캠을 킨다.)
@gzip.gzip_page
def detectme(request):
try:
cam = VideoCamera() #웹캠 호출
# frame단위로 이미지를 계속 송출한다
return StreamingHttpResponse(gen(cam), content_type="multipart/x-mixed-replace;boundary=frame")
except: # This is bad! replace it with proper handling
print("에러입니다...")
passdjango로 웹페이지에서 카메라를 켜는 방법에 대해 구글링을 해보면 이 정도 코드가 기본으로 나옵니다.
여기에서 쓸데없는 코드를 지우고, OpenPose를 사용하기 위한 코드를 추가해 보겠습니다.
3. OpenPose를 사용하기 위해 코드를 수정
일단 웹페이지 구조를 아래에 기술하겠습니다.
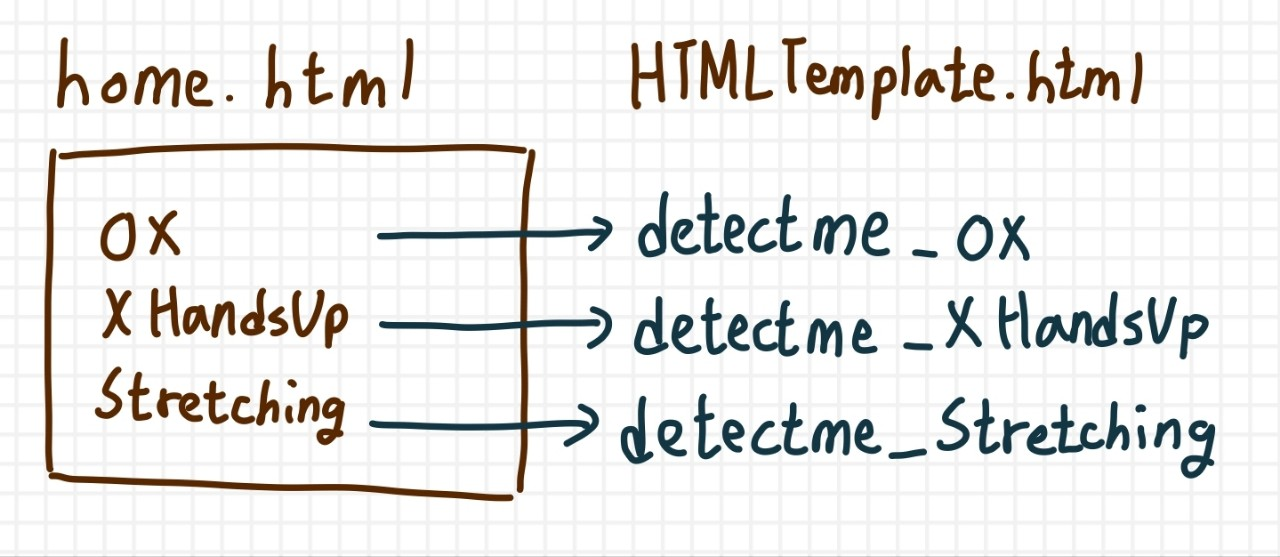
home.html에 OX, XHandsUp, Stretching 각 자세를 추정할 수 있는 링크를 연결했습니다.
# urls.py
from django.urls import path
from . import views
app_name="detectme"
urlpatterns = [
path('',views.home,name="home"),
path("detectme_OX",views.detectme_OX,name="detectme_OX"),
path("detectme_XHandsUp",views.detectme_XHandsUp,name="detectme_XHandsUp"),
path("detectme_Stretching",views.detectme_Stretching,name="detectme_Stretching"),
path('OX',views.OX,name="OX"),
path('XHandsUp',views.XHandsUp,name="XHandsUp"),
path('Stretching',views.Stretching,name="Stretching")
]위 링크는 urls.py 코드입니다.
아래는 home.html과 HTMLTemplate.html 코드입니다.
<!-- home.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Video...</h1>
<h3><a href="/OX">OX</a></h3>
<h3><a href="/XHandsUp">XHandsUp</a></h3>
<h3><a href="/Stretching">Stretching</a></h3>
</body>
</html><!-- HTMLTemplate.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>{{pose_type}}-Pose</h1>
<table>
<tr>
<td>
<img
src="http://127.0.0.1:8000/detectme_{{pose_type}}"
style="width: 320px; height: 240px"
/>
</td>
<td>
<h2><a href="/">돌아가기</a></h2>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
이제 가장 중요한 views.py를 살펴보도록 하겠습니다.
코드를 나누어 설명하면 가져다 쓰기 어려울 것 같아서 주석을 사용하여 설명하겠습니다.
이전 포스트에서 openpose에 대한 기본 코드는 숙지하고 있어야 이해하기가 쉽습니다.
# views.py
from glob import glob
from http.client import HTTPResponse
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect
from django.views.decorators import gzip
from django.http import StreamingHttpResponse
import cv2
from pathlib import Path
import playsound
import time
import threading
from django.urls import reverse
# MPII에서 각 파트 번호, 선으로 연결될 POSE_PAIRS
BODY_PARTS = { "Head": 0, "Neck": 1, "RShoulder": 2, "RElbow": 3, "RWrist": 4,
"LShoulder": 5, "LElbow": 6, "LWrist": 7, "RHip": 8, "RKnee": 9,
"RAnkle": 10, "LHip": 11, "LKnee": 12, "LAnkle": 13, "Chest": 14,
"Background": 15 }
POSE_PAIRS = [ ["Head", "Neck"], ["Neck", "RShoulder"], ["RShoulder", "RElbow"],
["RElbow", "RWrist"], ["Neck", "LShoulder"], ["LShoulder", "LElbow"],
["LElbow", "LWrist"], ["Neck", "Chest"], ["Chest", "RHip"], ["RHip", "RKnee"],
["RKnee", "RAnkle"], ["Chest", "LHip"], ["LHip", "LKnee"], ["LKnee", "LAnkle"] ]
# 각 파일 path
BASE_DIR = Path(__file__).resolve().parent
protoFile = str(BASE_DIR)+"/file/pose_deploy_linevec_faster_4_stages.prototxt"
weightsFile = str(BASE_DIR)+"/file/pose_iter_160000.caffemodel"
# 위의 path에 있는 network 모델 불러오기
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe(protoFile, weightsFile)
# openCV의 좌표계는 좌측위가 (0,0)이다...
# 아래/오른쪽으로 갈수록 증가한다
status=2
keep_time=[0,0,0]
O_X_HandsUp=["O","X","HandsUp"]
Success_Fail=["Success","Fail"]
return_result=""
############################################
# 1초마다 자세를 체크하도록 코드를 짰다. => threading.Timer 사용
def check_timer1(pose_type): #O,X,HandsUp
global keep_time,status
global return_result
if keep_time[0]==5 or keep_time[1]==5 or keep_time[2]==8:
result=show_result(pose_type,status) #O,X,HandsUp / Again
if result in O_X_HandsUp:
return_result=result
elif result=="Again":
keep_time[0]=keep_time[1]=keep_time[2]=0 #시간 초기화
elif keep_time[status]==0:
#다른 모션에서 바뀌어 들어옴
keep_time[0]=keep_time[1]=keep_time[2]=0
keep_time[status]+=1
elif keep_time[status]!=0:
keep_time[status]+=1
print(keep_time[0],keep_time[1],keep_time[2])
if return_result=="":
threading.Timer(1.0,check_timer1,(pose_type,)).start()
def check_timer2(pose_type): #Stretching
global keep_time,status
global return_result
if keep_time[0]==10 or keep_time[2]==8: # 자세유지 10초 하면 끝
result=show_result(pose_type,status) #Success / Fail
return_result=result
elif keep_time[status]==0:
#다른 모션에서 바뀌어 들어옴
keep_time[0]=keep_time[2]=0
keep_time[status]+=1
elif keep_time[status]!=0:
keep_time[status]+=1
print(keep_time[0],keep_time[1],keep_time[2])
if return_result=="":
threading.Timer(1.0,check_timer2,(pose_type,)).start()
##################################################
# 자세 체크 함수들
def check_HandsUp(points):
if points[0] and points[2] and points[3] and points[5] and points[6]:
head_x,head_y=points[0] #머리
rs_x,rs_y=points[2] #오른쪽 어깨
re_x,re_y=points[3] #오른쪽 팔꿈치
ls_x,ls_y=points[5] #왼쪽 어깨
le_x,le_y=points[6] #왼쪽 팔꿈치
#팔꿈치가 어깨보다 높을 것, 양 팔꿈치 사이에 머리가 위치할 것
if re_y < rs_y and le_y < ls_y and re_x < head_x and head_x < le_x:
if points[4] and points[7]:
rw_x,rw_y=points[4] #오른쪽 손목
lw_x,lw_y =points[7] #왼쪽 손목
#양쪽 손목 중, 어느 하나라도 머리보다는 위에 가야한다.
if rw_y<head_y or lw_y < head_y:
return True
else:
return False
else:
return False
else:
return False
else:
return False
def check_O(points):
if points[3] and points[4] and points[6] and points[7]:
re_x,re_y=points[3] #오른쪽 팔꿈치
rw_x,rw_y=points[4] #오른쪽 손목
le_x,le_y=points[6] #왼쪽 팔꿈치
lw_x,lw_y=points[7] #왼쪽 손목
#기본적으로 만세 조건을 만족시킬것 check_HandsUP()
#손목이 팔꿈치보다 안쪽에 위치할 것
#손목이 팔꿈치보다 위쪽에 위치할 것
if check_HandsUp(points) and ( (re_x<rw_x and rw_y<re_y) or (le_x>lw_x and le_y>lw_y) ):
return True
else:
return False
else:
return False
def check_X(points):
if points[0] and points[2] and points[3] and points[4] and points[5] and points[6] and points[7] and points[8]:
head_x,head_y=points[0] #머리
rs_x,rs_y=points[2] #오른쪽 어깨
re_x,re_y=points[3] #오른쪽 팔꿈치
rw_x,rw_y=points[4] #오른쪽 손목
ls_x,ls_y=points[5] #왼쪽 어깨
le_x,le_y=points[6] #왼쪽 팔꿈치
lw_x,lw_y=points[7] #왼쪽 손목
b_x,b_y=points[8] #골반(오른쪽)
#골반보다 팔꿈치가 위쪽에 위치 and 팔꿈치보다 손목이 위쪽에 위치 and 손목보다 머리가 위쪽에 위치
#어깨 안쪽으로 손목이 위치
if (b_y>le_y and b_y>re_y) and (le_y>lw_y and re_y >rw_y) and(lw_y>head_y and rw_y>head_y):
if rs_x<rw_x or lw_x<ls_x:
r_gradient=-1
l_gradient=1
if rw_x-re_x !=0:
r_gradient= (rw_y-re_y)/(rw_x-re_x)
if lw_x-le_x !=0:
l_gradient= (lw_y-le_y)/(lw_x-le_x)
if r_gradient<0 or l_gradient>0:
return True
else:
return False
else:
return False
def check_Stretching(points):
#오른쪽 골반, 오른쪽 무릎, 오른쪽 발목, 왼쪽 골반, 왼쪽 무릎, 왼쪽 발목
if points[8] and points[9] and points[10] and points[11] and points[12] and points[13]:
rh_x,rh_y=points[8] #오른쪽 골반
rk_x,rk_y=points[9] #오른쪽 무릎
ra_x,ra_y=points[10] #오른쪽 발목
lh_x,lh_y=points[11] #왼쪽 골반
lk_x,lk_y=points[12] #왼쪽 무릎
la_x,la_y=points[13] #왼쪽 발목
#기본적으로 O 조건을 만족시킬 것 check_O()
if check_O(points):
#오른쪽을 구부림
if rk_x<rh_x and rk_x<ra_x and ra_y<la_y:
return True
#왼쪽을 구부림
elif lk_x>lh_x and lk_x>la_x and la_y<ra_y:
return True
else:
return False
else:
return False
#################################################
# 결과를 반환하는 함수
def show_result(pose_type,status): #END/Again
if status==2: #status 2
if pose_type=="Stretching":
print("자세 유지에 실패하셨습니다.")
return "Fail"
else:
print("자세를 취해주세요.")
return "Again"
elif status==1: #status 1
print("X를 선택하셨습니다.")
return "X"
else: #status 0
if pose_type=="OX":
print("O를 선택하셨습니다.")
return "O"
elif pose_type=="XHandsUp":
print("만세를 선택하셨습니다.")
return "HandsUp"
elif pose_type=="Stretching":
print("자세유지에 성공하셨습니다.")
return "Success"
##################################################
class Openpose(object):
def __init__(self):
#self.video = cv2.VideoCapture(0) #for mac
self.video = cv2.VideoCapture(0,cv2.CAP_DSHOW) #for window
global status,return_result
status=2
return_result=""
def __del__(self):
self.video.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def get_frame(self,pose_type):
global status,return_result
self.status=status
_,frame = self.video.read()
inputWidth=320;
inputHeight=240;
inputScale=1.0/255;
frameWidth = frame.shape[1]
frameHeight = frame.shape[0]
inpBlob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, inputScale, (inputWidth, inputHeight), (0, 0, 0), swapRB=False, crop=False)
# network에 넣어주기
net.setInput(inpBlob)
# 결과 받아오기
output = net.forward() #추론을 진행할때 이용하는 함수
# 키포인트 검출시 이미지에 그려줌
points = []
for i in range(0,15):
# 해당 신체부위 신뢰도 얻음.
probMap = output[0, i, :, :]
# global 최대값 찾기
minVal, prob, minLoc, point = cv2.minMaxLoc(probMap)
# 원래 이미지에 맞게 점 위치 변경
x = (frameWidth * point[0]) / output.shape[3]
y = (frameHeight * point[1]) / output.shape[2]
# 키포인트 검출한 결과가 0.1보다 크면(검출한곳이 위 BODY_PARTS랑 맞는 부위면) points에 추가, 검출했는데 부위가 없으면 None으로
if prob > 0.1 :
cv2.circle(frame, (int(x), int(y)), 3, (0, 255, 255), thickness=-1, lineType=cv2.FILLED) # circle(그릴곳, 원의 중심, 반지름, 색)
cv2.putText(frame, "{}".format(i), (int(x), int(y)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255), 1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
points.append((int(x), int(y)))
else :
points.append(None)
#OX일때
if pose_type=="OX":
if check_O(points):
status=0
cv2.putText(frame, "choose O" , (50, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
elif check_X(points):
status=1
cv2.putText(frame, "choose X" , (50, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
else:
status=2
cv2.putText(frame, "None" , (50, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
#XHandsUp일때
elif pose_type=="XHandsUp":
if check_HandsUp(points):
cv2.putText(frame, "choose HandsUp" , (50, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
status=0
elif check_X(points):
status=1
cv2.putText(frame, "choose X" , (50, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
else:
status=2
cv2.putText(frame, "None" , (50, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
#Stretching일때
elif pose_type=="Stretching":
if check_Stretching(points):
status=0
cv2.putText(frame, "Keep going" , (50, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
else:
status=2
cv2.putText(frame, "None" , (50, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
#결과가 결정이 나면 반환
if return_result in O_X_HandsUp or return_result in Success_Fail:
return return_result
# 각 POSE_PAIRS별로 선 그어줌 (머리 - 목, 목 - 왼쪽어깨, ...)
for pair in POSE_PAIRS:
partA = pair[0] # Head
partA = BODY_PARTS[partA] # 0
partB = pair[1] # Neck
partB = BODY_PARTS[partB] # 1
#print(partA," 와 ", partB, " 연결\n")
if points[partA] and points[partB]:
cv2.line(frame, points[partA], points[partB], (0, 255, 0), 2)
#self.fps.update()
_, jpeg = cv2.imencode('.jpg', frame)
return jpeg.tobytes()
def gen(camera,pose_type):
#Stretching과 OX,XHandsUp의 timer가 다르다.
if pose_type=="Stretching":
check_timer2(pose_type)
else:
check_timer1(pose_type)
while True:
frame = camera.get_frame(pose_type)
#결과가 나오면 카메라를 끄고 반복문 break
if frame in O_X_HandsUp or frame in Success_Fail:
del camera
break
else:
yield(b'--frame\r\n'
b'Content-Type: image/jpeg\r\n\r\n' + frame + b'\r\n\r\n')
#########################################
# detectme 관련 함수들
@gzip.gzip_page
def detectme_OX(request):
try:
return StreamingHttpResponse(gen(Openpose(),"OX"), content_type="multipart/x-mixed-replace;boundary=frame")
except: # This is bad! replace it with proper handling
print("에러입니다...")
pass
@gzip.gzip_page
def detectme_XHandsUp(request):
try:
return StreamingHttpResponse(gen(Openpose(),"XHandsUp"), content_type="multipart/x-mixed-replace;boundary=frame")
except: # This is bad! replace it with proper handling
print("에러입니다...")
pass
@gzip.gzip_page
def detectme_Stretching(request):
try:
return StreamingHttpResponse(gen(Openpose(),"Stretching"), content_type="multipart/x-mixed-replace;boundary=frame")
except: # This is bad! replace it with proper handling
print("에러입니다...")
pass
##########################################
# 링크 관련 함수들
def home(request):
return render(request,"home.html") #home.html을 호출해서 띄워준다.
def HTMLTemplate(request,pose_type):
return render(request,"HTMLTemplate.html",{"pose_type":pose_type})
def OX(request):
pose_type="OX"
return HttpResponse(HTMLTemplate(request,pose_type))
def XHandsUp(request):
pose_type="XHandsUp"
return HttpResponse(HTMLTemplate(request,pose_type))
def Stretching(request):
pose_type="Stretching"
return HttpResponse(HTMLTemplate(request,pose_type))위의 코드에서 자세를 판단하는 함수들이나 timer 부분은 여러분의 프로젝트의 맞게 알아서 구현하시면 됩니다.
중요한 코드는 OpenPose 클래스와 gen() 함수 부분입니다.
(어느 기술 블로그, 깃허브를 찾아봐도 이 두 개는 반드시 포함되어 있습니다.)
4. OpenPose with Django를 프로젝트에 사용하지 못한 이유
솔직히 말하자면.... 위의 코드를 어느 정도 짰을 때, 개발이 어느 정도 끝났구나 하는 안도감이 들었습니다.
하지만 배포를 하고 보니 큰 문제점이 있다는 것을 깨달았습니다.
위 코드를 백엔드에 붙여서 같이 배포를 했는데, 도저히 카메라가 켜지지 않는 상황이 발생했습니다.
왜 그런지 곰곰이 생각해 보았습니다.
위 코드에서 카메라를 켜는 코드가 있습니다.
그런데 저 코드는, 코드가 돌아가는 컴퓨터의 웹캠을 켜는 코드입니다.
즉, 사용자의 웹캠을 키는 것이 아니라 서버의 웹캠을 켜게 되는 것입니다.
device가 특정된 프로젝트라면 aws에 카메라를 등록하여 사용할 수 있겠지만, 저희 프로젝트의 경우 어떤 device를 사용하여 접속하든 서비스를 이용할 수 있어야 합니다.
이 문제를 해결하기 위해 구글링을 해보니, RSTP를 사용하는 방법이 있었습니다.
하지만 졸프가 거의 끝나가는 시점에 이 문제를 맞닥뜨린 저희 팀은 RSTP를 사용하기가 힘들었습니다.
저희 팀은 배포가 좀 더 쉽도록 프론트와 연결이 쉽게 js코드로 모션인식을 하기로 했습니다.
그래서 사용하기로 한 것이 PoseNet입니다.
이에 대해서는 다음 포스트에 적도록 하겠습니다.
'프로젝트 > 졸프 - 참여형 동화 서비스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [모션인식] PoseNet을 사용하여 실시간으로 자세 인식하기 (4) | 2022.05.11 |
|---|---|
| [모션 인식] Python과 OpenPose(OpenCV)를 사용하여 실시간 자세 추정하기 (11) | 2022.05.07 |
| [모션 인식] Teachable Machine으로 자세 추정하기 (0) | 2022.05.06 |
| 참여형 동화 서비스 - 주제 변경 (0) | 2022.05.05 |
| 참여형 동화 서비스 - NLP(KoGPT2) (9) | 2021.11.25 |